USD/INR rallies further amid continuous foreign outflows, India's PMI cools down
- The Indian Rupee continues to decline against the US Dollar amid consistent FIIs selling in the Indian stock market.
- India’s HSBC Composite PMI drops to 58.9 in November from 59.7 in October.
- Investors await the US NFP data for fresh cues on the Fed’s monetary policy outlook.
The Indian Rupee (INR) extends its losing streak for the fourth trading day against the US Dollar (USD) on Tuesday. The USD/INR pair stretches its bull run to near 91.45 as the continuous outflow of foreign funds from the Indian stock market amid trade frictions between the United States (US) and India has remained a major drag on the Indian Rupee.
A report from Reuters has also shown that the USD/INR pair has remained firm due to strong dollar demand linked to likely maturity of positions in the non-deliverable forwards (NDF) market and continued foreign portfolio outflows.
So far this month, Foreign Institutional Investors (FIIs) have offloaded stake worth Rs. 21,073.83 crore in the Indian equity market, while remaining net sellers in all trading days.
Meanwhile, better-than-projected India’s Trade Deficit Government data for November has failed to lift investors’ sentiment toward the Indian Rupee. On Monday, the data showed that India’s merchandize trade deficit shrank to $24.53 billion from $41.68 billion in October, beating a Reuters poll estimate of $32 billion. The trade deficit report also showed that India’s overall goods exports for November rose 19%, largely contributed by a 22.6% increase in merchandize transport to the US.
On the economic data front, India’s HSBC Composite Purchasing Managers’ Index (PMI) dropped to 58.9 from 59.7 in November, suggesting that the overall business activity expanded but at a moderate pace. The overall private sector output growth cooled down due to a slowdown in both manufacturing and the service sector activity.
The table below shows the percentage change of Indian Rupee (INR) against listed major currencies today. Indian Rupee was the weakest against the Japanese Yen.
| USD | EUR | GBP | JPY | CAD | AUD | INR | CHF | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| USD | -0.06% | -0.08% | -0.23% | -0.03% | -0.03% | 0.22% | -0.02% | |
| EUR | 0.06% | -0.02% | -0.16% | 0.02% | 0.02% | 0.30% | 0.04% | |
| GBP | 0.08% | 0.02% | -0.19% | 0.04% | 0.03% | 0.28% | 0.05% | |
| JPY | 0.23% | 0.16% | 0.19% | 0.22% | 0.21% | 0.46% | 0.23% | |
| CAD | 0.03% | -0.02% | -0.04% | -0.22% | -0.00% | 0.27% | 0.02% | |
| AUD | 0.03% | -0.02% | -0.03% | -0.21% | 0.00% | 0.29% | 0.03% | |
| INR | -0.22% | -0.30% | -0.28% | -0.46% | -0.27% | -0.29% | -0.26% | |
| CHF | 0.02% | -0.04% | -0.05% | -0.23% | -0.02% | -0.03% | 0.26% |
The heat map shows percentage changes of major currencies against each other. The base currency is picked from the left column, while the quote currency is picked from the top row. For example, if you pick the Indian Rupee from the left column and move along the horizontal line to the US Dollar, the percentage change displayed in the box will represent INR (base)/USD (quote).
Daily digest market movers: US Dollar trades with caution ahead of US NFP data
- The Indian Rupee remains on the back foot against the US Dollar, even as the latter underperforms broadly ahead of the US Nonfarm Payrolls (NFP) combined report for October and November, which will be published at 13:30 GMT.
- At the press time, the US Dollar Index (DXY), which tracks the Greenback’s value against six major currencies, trades tightly close to the eight-week low of 98.13 posted on Thursday.
- Investors will closely monitor the US employment data as it will influence market expectations for the Federal Reserve’s (Fed) monetary policy outlook. The Fed has reduced its interest rates by 75 basis points (bps) this year, and comments from members have signaled that the major driver behind rate cuts was weak labor market conditions.
- On Monday, New York Fed Bank President John Williams said at an event hosted by the New Jersey Bankers Association that the “monetary policy is very focused on balancing jobs," adding that the labor market “is clearly cooling”.
- According to expectations, the US Unemployment Rate remained steady at 4.4% in November. Signs of further weakness in employment conditions would prompt Fed dovish expectations, while indication of an improvement might weigh on the same.
- According to the CME FedWatch tool, there is a 67% chance that the Fed will cut interest rates at least two times by the end of 2026.
Technical Analysis: USD/INR stays above 20-day EMA
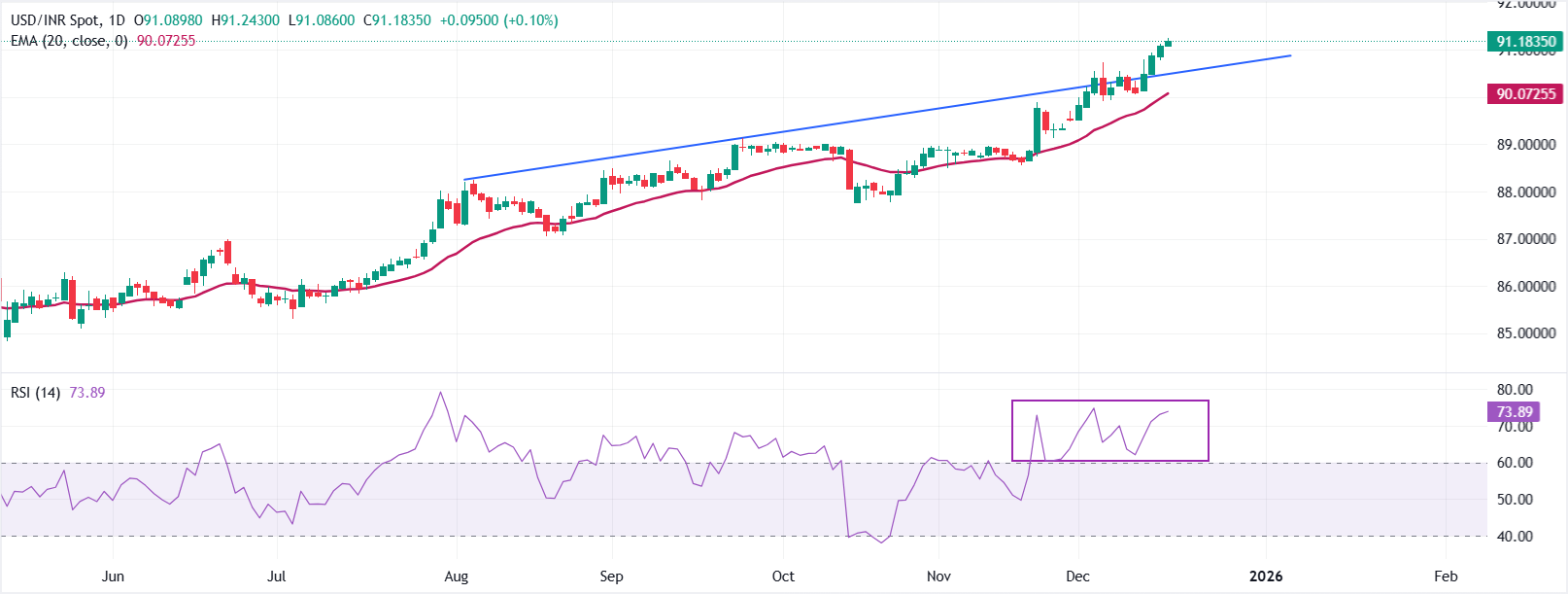
USD/INR trades around 91.45 on Tuesday, the highest level seen ever. Upward-sloping 20-day Exponential Moving Average (EMA) at 90.0726 supports the bullish bias, with pullbacks expected to hold on first tests of the average.
The 14-day Relative Strength Index (RSI) at 73.89 is overbought, demonstrating strong momentum with signals pointing stretched conditions that could temper immediate upside.
The upward-sloping average should act as first support on dips, while a daily close below it would signal a deeper correction toward the round-level figure of 90.00. Looking up, a sustained strength above the current level would extend the advance toward 92.00.
(The technical analysis of this story was written with the help of an AI tool)
Indian economy FAQs
The Indian economy has averaged a growth rate of 6.13% between 2006 and 2023, which makes it one of the fastest growing in the world. India’s high growth has attracted a lot of foreign investment. This includes Foreign Direct Investment (FDI) into physical projects and Foreign Indirect Investment (FII) by foreign funds into Indian financial markets. The greater the level of investment, the higher the demand for the Rupee (INR). Fluctuations in Dollar-demand from Indian importers also impact INR.
India has to import a great deal of its Oil and gasoline so the price of Oil can have a direct impact on the Rupee. Oil is mostly traded in US Dollars (USD) on international markets so if the price of Oil rises, aggregate demand for USD increases and Indian importers have to sell more Rupees to meet that demand, which is depreciative for the Rupee.
Inflation has a complex effect on the Rupee. Ultimately it indicates an increase in money supply which reduces the Rupee’s overall value. Yet if it rises above the Reserve Bank of India’s (RBI) 4% target, the RBI will raise interest rates to bring it down by reducing credit. Higher interest rates, especially real rates (the difference between interest rates and inflation) strengthen the Rupee. They make India a more profitable place for international investors to park their money. A fall in inflation can be supportive of the Rupee. At the same time lower interest rates can have a depreciatory effect on the Rupee.
India has run a trade deficit for most of its recent history, indicating its imports outweigh its exports. Since the majority of international trade takes place in US Dollars, there are times – due to seasonal demand or order glut – where the high volume of imports leads to significant US Dollar- demand. During these periods the Rupee can weaken as it is heavily sold to meet the demand for Dollars. When markets experience increased volatility, the demand for US Dollars can also shoot up with a similarly negative effect on the Rupee.



